Determining the number of test fires needed to represent the variability present within 9mm Luger firearms
Abstract
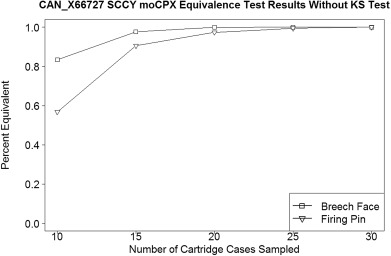
Many studies have been performed in recent years in the field of firearm examination with the goal of providing an objective method for comparisons of fired cartridge cases. No published research to support the number of test fires needed to represent the variability present within the impressions left on a cartridge case could be found. When a suspect firearm is submitted to a firearm examiner, typically two to four test fires are performed. The recovered cartridge cases are compared to each other to determine which characteristics from the firearm are reproducing, and then compared to any cartridge cases collected at a crime scene. The aim of this research was to determine the number of test fires examiners should perform when a suspect firearm is submitted to the lab to balance cartridge case acquisition time with performance accuracy. Each firearm in the IBIS® database at West Virginia University® is represented by approximately 100 fired cartridge case entries. Random samples of cartridge cases were taken separately from the breech face match score and firing pin match score lists. This subset was compared to the total match distribution of the firearm using a hybrid equivalence test to determine if the subset of similarity scores were statistically equivalent to the larger distribution of scores. For the sampled distribution to remain above 80% equivalent to the match distribution, a minimum of 15 cartridge cases should be used to model the match distribution, based on IBIS® scores. Thirty cartridge cases is a conservative estimate, allowing one to determine that the location and dispersion of the match and sampling distributions are equivalent with nearly 100% probability.